The basic unit for storing data is variable. One variable, however, can contain only one value at a time when the program gets executed. When we need to handle a large number of data simultaneously, it requires a special way of working with them, which enables relatively easy access, removal, search, and similar operations with individual data. For this, we can use Java data structures.
This chapter discusses Java’s most basic data structure, called an array.
Arrays in Java
An array is a data structure representing a numbered array of variables of the same type. Individual variables in an array are called elements, and their number(location) in an array is called an index.
The total number of elements of the array is called the array’s length.
We can store only the fixed size of elements in the Java array. Once we specify its length, it cannot be changed.
In Java, the numbering of array elements starts from zero. That means if it’s n array length, then the index of the elements can be in the interval of 0 to n – 1. All elements of the array must be of the same type. There are no restrictions for the type of array elements — it can be either primitive or class.
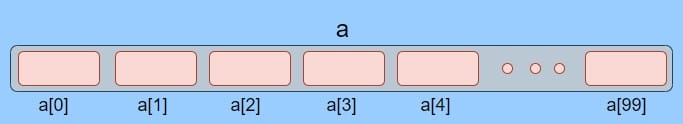
Here we have an array that contains 100 elements. See how the first has an index of 0 and the last 99.
We can access each element of an array by specifying the array’s name and its index in parentheses.
e.g. a[0], a[1], a[25]. a[79] …
There are two types of arrays in Java:
- One-Dimensional array
- Multidimensional array
In this lesson, we’ll cover the One-Dimensional arrays.
One-Dimensional Array in Java
A one-dimensional array uses a single index to store elements.
Declaring an array in Java
class Test {
int[] a;
int b[];
int []c;
}
Here we have three valid ways to declare an array in Java. The important part is to put [] parentheses, which tell Java that the variable will actually be an array. Since we put an int, this means that an array will only contain elements of the int type.
Instantiation and Initialization of Java Array
Here are the different ways to initialize arrays:
class Test {
int[] a = new int[100];
int b[] = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] c = {1, 2, 3};
}
All three ways are valid. We can initialize the array by immediately specifying its length in parentheses and assigning values to it. After initialization, we cannot add new elements to this array since it will have a fixed length.
Let’s see one example when we first initialize it and then add elements:
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize the array
int[] a = new int[3];
// add elements to array
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 2;
a[2] = 3;
}
}
In the above example, we initialized the array a and assigned it a length of 3. After that, we added elements from index 0 to index 2.
After initialization, all three elements will have a value of 0 because that is the default value for the int type.
Accessing array elements
We can access the elements of an array through the name of the array and specifying the index of the element within parentheses:
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// initialize the array
int[] a = new int[3];
// add elements to array
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 2;
a[2] = 3;
// accessing the array elements
System.out.println(a[0]);
System.out.println(a[1]);
System.out.println(a[2]);
}
}
We can access its length by calling the arrayName.length.
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[10];
System.out.println(array.length);
}
}
Java Arrays Examples
Passing Array to a method in Java and retrieving the element
class Test {
public static String getSecondElementOfArray(String[] strArray) {
return strArray[1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] array = {"one", "two", "three", "four", "five"};
String secondElement = getSecondElementOfArray(array);
System.out.println("The second element is: " + secondElement);
}
}
Add fewer elements to an array than it can support
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] array = new String[2];
array[0] = "one";
System.out.println(array[0]);
System.out.println(array[1]);
}
}
Going through array elements using Java for loop
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] array = {"one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "size", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"};
for (String element : array) {
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[2];
array[0] = 1;
array[1] = 2;
array[2] = 3; // this line will cause the exception
}
}