Recursion in Java is the process in which the method calls itself. These methods are called recursive methods.
We use Recursion when some process needs to be repeated a number of times.
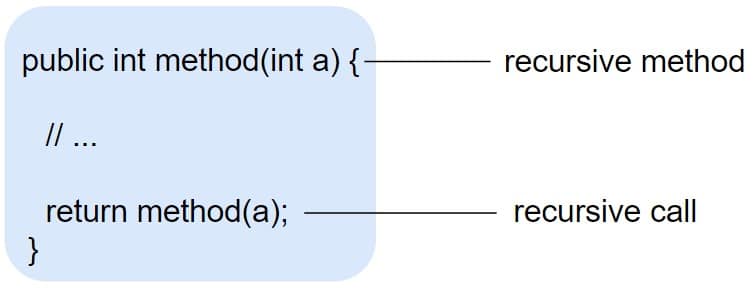
Let’s see some examples:
Examples of a Recursion in Java
Recursive method
public void printData(int data) {
System.out.println(data);
printData(data);
}
See how this method calls itself. In this case, the data value will be printed until we hit the java.lang.StackOverflowError.
As you can guess, this is not a good way to write a recursive method. We need to have the code which will stop the execution when a certain condition is being met, to avoid calling the method infinitely.
Let’s add it:
public static void printData(int data) {
if (data > 0) {
System.out.println(data);
printData(--data);
}
}
Now, if we pass the value 5, the method will call itself as long as the value is greater than zero.
Output: 5 4 3 2 1
Calculate factorial of the given number
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(factorial(5));
}
static int factorial(int num) {
if (num == 1) {
return 1;
} else
return (num * factorial(num - 1));
}
}
Output: 120
Fibonacci Series for the given number
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int maxNumber = 15;
for (int i = 0; i < maxNumber; i++) {
System.out.print(fibonacci(i) + " ");
}
}
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1);
}
}
Output: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377
That was all about Recursion in Java. Proceed to the next lesson.
Happy coding!